
by Connor Madsen | Mar 31, 2017 | Industry Intel
The Cyber News Rundown brings you the latest happenings in cyber news weekly. Who am I? I’m Connor Madsen, a Webroot Threat Research Analyst, and a guy with a passion for all things security. Any more questions? Just ask.
Ransomware Exploits Safari Bug
Apple fixed a flaw earlier this week that allowed scammers to exploit a pop-up redirecting porn viewers to a fake law enforcement page. Once there, further access was blocked, and a demand for an iTunes gift card as ransom was made. While many unsuspecting users fell victim to the scam, Apple was able to promptly issue a patch that resolved the vulnerability. Apple has also recommended that anyone affected by the scam should clear their browser cache, to remove any possibility of relaunching the malicious sites.
Microsoft’s Docs.com Sharing Documents Publicly
Researchers have discovered that a vast majority of the documents posted to Docs.com are fully searchable and indexed into several search engines. This wouldn’t be such an issue if the many users posting content to the site were aware of the public availability of the possibly-sensitive documents they had unwittingly sent through their organizations and out into the public domain. While Microsoft has since removed the search bar from the main site page, anything uploaded prior is still available through multiple search engines.
Hong Kong Voter Records Leaked
As the Hong Kong elections took place over the weekend, two laptops containing sensitive information for Hong Kong’s nearly 3.7 million voters were stolen from a backup location for the elections. While the data on the laptops was encrypted, it could only be a matter of time until it is broken and that data is exposed. If released, it would be the largest data breach to ever come out of Hong Kong.
Crusader Adware Replaces Tech Support Search Results
A new browser extension has been discovered that can modify a user’s search results, launch additional ads, and even display pop-ups for other scams. Usually installed with a bundle of other software, the extension known as Crusader is able to monitor all Internet traffic and rewrite tech support numbers to continue the cycle by having the victim contact yet another tech support scammer for “assistance.”
WoW Users Targeted with Phishing Attack
Many avid World of Warcraft players have received emails offering an in-game pet that was “gifted” to them by a fellow gamer. Unfortunately for the recipients, the link directing them towards the Battle.net site to claim their gift actually sent them to a phishing site set up to capture all of their login information. While the scam site is already blocked by Google’s Safe Browsing, users are still urged to proceed with caution, should they receive any suspicious emails.

by Blog Staff | Mar 31, 2017 | Home + Mobile
Don’t wait for a system failure, ransomware attack, or for your laptop to be stolen before you start thinking about backing up your data.
Why back up?
According to a 2016 study by Acronis, 1 in 3 people have suffered data loss and are willing to pay up to $500 or more to recover lost files. Your data and important files are undoubtedly worth a lot to you, but—realistically speaking—just how much are you willing (or even able) to shell out?
With the increase in ransomware and sophisticated attacks, you can’t afford NOT to back up your files and sensitive data. Being proactive with your backup can help save your favorite vacation photos, videos of your kid’s first piano recital, not to mention sensitive information that could cost you thousands by itself.
In an effort to help the community be more cyber aware, WorldBackupDay.com celebrates on March 31st not only as a day for backing up your personal data, but a day for preserving our increasingly digital heritage for future generations.

How to effectively back files up to prevent data loss:
- Choose a secure backup solution. Whether it’s a cloud-based service or an external hard drive, do your research and choose what’s right for you.
- Implement a backup schedule that covers your preferred data through your cloud solution or external drive.
- Set reminders to ensure that your backups are running regularly and that they haven’t encountered any errors.
I’ve backed up my data. Now what? How do I avoid a ransomware attack?
“Throughout 2016 and likely into 2017, the Office document macro infection into encrypting ransomware was quite common. By disabling macros completely in the trust center (free and easy to do) you will completely remove this attack vector from posing a threat to you or your organization.” –Tyler Moffitt, Senior Threat Research Analyst
- Disable macros
- Keep your device and all programs, plugins, add-ons, and patches up to date
- Use a secure browser with an ad blocking plugin
- Disable autorun in Windows
Take the Pledge
Hop on the World Backup Day bandwagon. Share a Tweet to help keep yourself, your friends, and your family protected from ransomware attacks, stolen devices, and system failure.
It’s easy. Repeat after me.
“I solemnly swear to backup my important documents and precious memories on March 31st.”

by Blog Staff | Mar 28, 2017 | Home + Mobile
Ransomware authors are pivoting their attacks from individuals to government entities and health care institutions, causing a threat to public safety. Traditionally, crypto ransomware targeted individuals and encrypted their personal data and files as a form of extortion for hundreds of dollars. Ransomware has evolved to target businesses and government agencies for much larger financial gains.
The cost of ransomware
There are countless news stories of hospitals and other institutions being shut down by ransomware. We have been seeing an increase in attacks on government entities, including counties and police departments.
A small Ohio town experienced a ransomware attack earlier this year that shut down county government offices and 911 dispatch. This slowed their emergency response but luckily they were still able to respond to emergency 911 calls.
The financial costs to these organizations are also a concern and they’ve been steadily increasing as crypto ransomware continues to evolve.
The FBI estimated that cybercriminals would collect over $1 billion in ransoms during 2016.
In reality, the actual losses suffered by organizations are much higher due to the disruption of productivity and when government entities and police departments are increasingly being targeted, public safety becomes an issue.
An issue of public safety
Ransomware attacks targeting hospitals are increasing, crippling critical infrastructure and exposing or hindering Electronic Health Records (EHR). When these records are impacted, it causes patient care to be hindered or halted. As more organizations implement connected medical devices and allow employees to bring their own devices to work, access points for unauthorized users are left open.
A 2016 study by Peak 10 found that only 47% of current healthcare organizations have implemented advanced malware protection and only 57% have implemented an encrypted network.
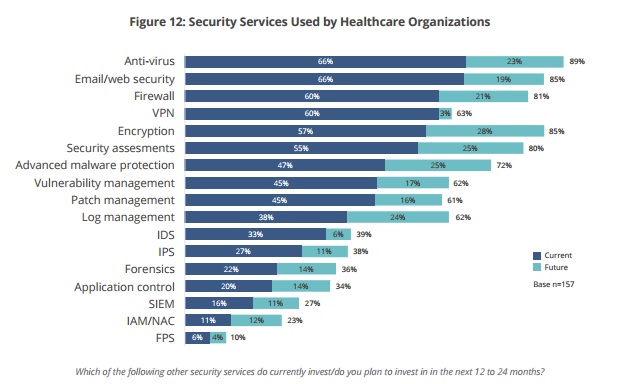
Earlier this year, an attack on police CCTV cameras in Washington D.C. crippled the city’s surveillance system and forced major citywide reinstallation. Although this attack was an extortion effort, it makes you wonder how similar attacks will be used to cripple government emergency response and how cyberattack methods are evolving.
Once ransomware hits a police department’s system, the damage can be catastrophic if mitigation methods aren’t in place. Attacks cripple dispatch systems and patrol car computers, slow police response time, expose records, and create an unsafe environment for officers in inmate holding areas.
What the government is doing about it
Ransomware and other cyberattacks on government operations are a real issue of public safety and steps need to be taken to improve response time to such attacks. The FBI recommends taking prevention and continuity measures to lessen the risk from ransomware attacks.
- Back up your data locally or in the cloud
- Secure backups and keep them on scheduled updates
- Do not open attachments in unsolicited emails
- Keep your operating system, software, and firmware up-to-date
- Ensure antivirus and antimalware solutions are set to automatically scan and update
- Report internet crimes to the Internet Crime Complaint Center (IC3)
Ransomware presents a real, imminent threat to the public and to our government. Share this article to help spread ransomware awareness in your community.

by Connor Madsen | Mar 24, 2017 | Industry Intel
The Cyber News Rundown brings you the latest happenings in cyber news weekly. Who am I? I’m Connor Madsen, a Webroot Threat Research Analyst, and a guy with a passion for all things security. Any more questions? Just ask.
Hackers Threaten to Lock 200M+ iCloud Accounts
Hackers are threatening to remotely lock down over 200 million iCloud accounts. Webroot Senior Threat Research Analyst, Tyler Moffitt told SC Media that this may be a bluff. We’ll wait and see on this one since all we have to go off of is the hackers’ word and a few screenshots. We’ll know more as the ransom deadline of April 7th approaches.
American Farmers are Hacking Their Tractors
This isn’t our usual data leak or ransomware attack, it’s black market tractor hacking. Farmers are taking things into their own hands in an effort to thwart manufacturer blocks on their farming equipment. These blocks are an attempt to prevent farmers from going to cheaper, “unauthorized” repair shops to maintain their vehicles. Farmers are starting to hack their equipment with Ukrainian Firmware so they can fix their tractors when they need to and at an affordable price.
ISPs Now Allowed to Sell User Browsing History to Advertisers
It just wouldn’t be the Cyber News Rundown without a new government data leak or citizen privacy battle. The US Senate has voted to eliminate broadband privacy rules that require ISPs to obtain customer consent before selling any sensitive information with advertisers. The vote was split equally down the party lines, and now only a House vote or Presidential veto could stop the roll-back of the privacy rules. The data in question is extremely valuable as major corporations could use it to pattern out an individual’s entire day, based on their Internet usage, purchases made, and places visited.
UK Mobile Data Breach Leaves Customers Stunned
Customers at Three UK found a surprise when signing into their accounts, a breach of privacy where they’d see a stranger’s personal information and call history. The cause of the breach hasn’t been announced but this is their second data exposure within a few months. Although the Three UK breach only affected a small percentage of their 9 million customers, I’m guessing back-to-back data leaks are not helping their retention rates.
McDonald’s Delivery App Vulnerabilities
The McDonald’s India-exclusive app service, McDelivery, is currently under fire for an API leak that has exposed millions of users. The vulnerability was originally reported to McDonald’s in early February and is still unpatched. While reporting these types of breaches isn’t mandatory in India, you’d think the sheer number of users who could be negatively impacted would motivate McDonald’s to release an update. I guess I wouldn’t mind people knowing how often I order off the dollar menu either — but having access to my phone number and address is another story.
by Blog Staff | Mar 23, 2017 | Home + Mobile
Aren’t you tired of annoying pop-ups that slow your computer way down, or give you viruses that cripple your PC faster than De’Aaron Fox on a fast break? What if we said you could make minor changes to your lineup to drastically speed up browsing sessions, improve browser security, and reduce your risk of downloading malware or potentially unwanted applications (PUAs)?
Well, hold onto your hats, folks. That’s exactly what I’m going to do. (Just think of all the time and hassle you’ll save when you no longer have to remove junk programs from your parents’ computers due to accidental pop-up clicks!)
Recommended Browsers for Privacy & Security
Personally, I’m a fan of Google Chrome and Opera, but I also use the most up-to-date versions of Waterfox and Internet Explorer for testing purposes or when accessing certain content management systems. Each of the below have quality security features, including pop-up blockers, antispyware, antivirus, anti-phishing, and private modes that complement a full antivirus and cybersecurity solution. Here’s a breakdown.
Google Chrome: I’m biased here, but Chrome is extremely stable, has cross-platform functionality, and it’s pretty darn fast if you have enough RAM or a gaming PC like myself. Most importantly, however, it offers a wide range of extensions for improved user experience and navigation, handling pop-ups and ads, etc. If you’re a fellow Chrome user, I can’t recommend Adblock Plus enough. It’s amazing how quickly pages load when they’re not cluttered up with ads you’d never intentionally click on anyway.
Waterfox: Firefox was a longtime favorite of mine for a variety of reasons, but we’ve grown apart in recent years. Let’s face it: back when we first met, Firefox looked good, moved fast, and had better functionality than anything else available. These days, Firefox has gotten sluggish and imposes too many restrictions. (And let’s not forget the incessant update phase from a few years back.) My new side-browser is Waterfox. If privacy is a concern, you’ll be happy to hear that absolutely no data is sent back to Firefox or Waterfox. You can also sleep better at night knowing that Waterfox is partners with Ecosia, a search engine provider that plants trees with earned revenue. Built on the same Firefox code but without the painful restrictions, it reminds me why I ever fell in love with Firefox in the first place.
Opera: Maybe it sounds crazy, but Opera is my favorite mobile browser. I get impatient about slow network speeds and Wi-Fi connections, especially when my ISP throttles my bandwidth. Opera is super-fast and has plenty of features, but what really makes it stand out for mobile is its Turbo Mode. Turbo Mode compresses web traffic through Opera’s servers, reduces the amount of data transferred, AND it dodges annoying ISP restrictions. Opera has built-in fraud and malware protection that’s enabled by default. It uses several databases and blacklists for known phishing and malware websites to help with browser security.
Internet Explorer: If I’m being honest, I wouldn’t say I like IE. But the reason it’s on this list is that it’s still a shockingly popular browser, and a lot of content management systems and other programs I’m required to use professionally run more smoothly with IE. You can adjust security levels, enable the SmartScreen Filter, and enable ActiveX filtering for enhanced browser security on Internet Explorer.
How to Secure your Browser
Having layers of protection is never a bad idea, especially with the evolving threats we’re faced with today. Preventing pop-ups is a quick and easy step to protect yourself and any family members you may have who aren’t as up-to-date on mitigation techniques. Built-in antispyware and anti-phishing components of these browsers typically notify users when they click malicious or risky URLs, thereby stopping attacks before the actual malware or spyware is downloaded onto your machine.
By using secure browsers on all your devices, in addition to cloud-based cybersecurity, you can avoid many of the threats on the web, and seriously up your internet security game.

by Blog Staff | Mar 21, 2017 | Home + Mobile
Sometimes it takes a close call or bad experience to really hammer it home. The concept of identity theft is nothing new. To put it in perspective, my step-dad had his identity stolen, and didn’t even know it. He was targeted by a social engineering attack and forked over several hundred dollars during the scam and didn’t realize he was a victim until I sat down with him to help speed up his aging computer.
What is social engineering?
Social engineering attacks, like any con, are based on psychological manipulation to incite victims to give up money and sensitive, confidential information. An example given by Wikipedia (yes, we use Wiki too), might be someone who walks into a building and posts an official-looking flyer on the company bulletin that announces a new phone number for the help desk. When employees call for help, the criminal might ask for passwords and other corporate login credentials. This opens access to the company’s private information. Another example of social engineering might involve a hacker contacting their target on a social network, such as Facebook. They start a conversation and gradually gain their target’s trust, then use that trust to get access to sensitive information.
Why? Because $$$.
Motives typically involve some kind of financial gain, though some attackers choose victims for personal reasons, such as revenge. In my step-dad’s case, it all started with that slow computer. He signed up for a sketchy PC cleaner tool to get rid of viruses and speed things up, after which he was targeted through a phishing scam. This attack resulted in him paying the attacker sums of $150 to $300 on various separate occasions.
What are the most common types of social engineering attacks?
Phishing: These attacks can include scenarios like the aforementioned, but may also be more targeted. Spear phishing attacks are more sophisticated and can include customized email sends or targeted ads that require a bit more research on the attacker’s part.
Watering hole: In a watering hole attack, user-groups are specifically being targeted. For example, attackers would research specific employees that visit niche websites and then host malware specifically targeting these employees.
Baiting: Just like the term suggests, baiting attacks involve offering victims something they want. Most often, these appear on peer-to-peer sharing sites where you can download or stream those hot new movies or Beyonce tracks you’ve been hearing about. The risk is that you may be downloading malware instead of, or in addition to, the files you actually want. Baiting can also include too-good-to-be-true online deals or fake emails with answers to questions you never asked on any forums.
Who and what to trust
Social engineering attacks are limited only by the attacker’s imagination. But, that means knowledge is your greatest tool against evolving cyber threats. I’m not suggesting you turn paranoid, but if something online strikes you as a little off or too good to be true, question it. Don’t remember sending a package or signing up for a contest? Then don’t click the “track my package” or the “Congrats, you’re a winner!” links.
Phishing and baiting tactics have been used in recent employment scams targeting recent college graduates. Whether you’re on social media, applying for jobs, or simply surfing the web, always think before you click, do your research, and visit HTTPS sites through a secure search engine, not via email or social media links.

by Connor Madsen | Mar 17, 2017 | Industry Intel
The Cyber News Rundown brings you the latest happenings in cyber news weekly. Who am I? I’m Connor Madsen, a Webroot Threat Research Analyst, and a guy with a passion for all things security. Any more questions? Just ask.
USAF Leaks Highly Sensitive Data
Our government is back at it again. Researchers discovered the exposure of an unsecured backup drive containing names, addresses, ranks, and Social Security numbers of over 4,000 United States Air Force officers and top security clearance information of other high-ranking officials. Personal records for several celebrities who had undergone security clearance checks prior to visiting foreign military bases were also exposed. It sounds like this breach could prove to be disastrous if the information gets into the hands of enemies to the United States.
Ohio County Facing Massive Ransom
In recent weeks, Ohio County officials have been recovering from a cyber-attack that forced the county to shut down over 1,000 computers to prevent the infection from spreading. The ransom for the return of their files was 28 bitcoins, roughly $35,000 at the time of writing, which the county correctly chose to ignore and instead restored their systems from backups. While the whole process cost the county nearly $50,000, the situation could have been worse if they paid and received nothing in return for paying the ransom.
Instagram Credentials at Risk
Researchers discovered 13 seemingly harmless apps on the Google Play Store that function as data collectors for your personal information. The apps themselves claim to increase your Instagram follower numbers by simply having users log into their accounts, only to be greeted with an error message. Fortunately, Google has already been made aware of the Turkish-based apps and has removed them.
PetrWrap Circumvents Ransomware Authors’ Cut of Ransom
As ransomware continues to evolve, some malware authors have begun acting against their peers, who wish to piggyback off the creations. By exploiting a bug found in the Petya ransomware variant, a new collection of cybercriminals have created a workaround to insert their own encryption keys over the Petya authors’ and collect the ransom themselves. This workaround comes months after Petya creators implemented methods to stop this very exploitation of their software.
New Updates on Phishing Tactics
People have been on the watch for tax-related phishing scams, as they appear around this time every year. The latest trend, however, appears to be PDF files that do not contain malicious code and use social engineering to direct victims towards compromised websites to input sensitive information. Additionally, there has been a recent influx of phishing attacks due to fake friend requests through email, as users are exceedingly likely to click on these types of links and attempt to “log in” to view the request.

by Blog Staff | Mar 15, 2017 | Home + Mobile
The online threat landscape continues to evolve. Not only do we need to continue innovating and refining our protection techniques, but we also need to stay on top of our cybersecurity education in order to protect each other from these attacks. As it happens, a number of people still don’t use any cybersecurity on their personal devices. To better understand these patterns, and to help create a cybersmart community as more aspects of our daily lives become internet-connected, we took it upon ourselves to gather data from home users in the form of a survey.
First, how many people use cybersecurity?
We found that 14% of users surveyed don’t use any cybersecurity protection whatsoever. Sure, we could tell you all you should be using our cloud-based SecureAnywhere® protection, but, in all honesty, it’s more important to us that people protect themselves in the first place, whether they’re our customers or not. You can help your friends become CyberSmart by sharing this blog or by sending a Tweet to your network. Foregoing an antivirus solution and neglecting to layer your cyber defenses exposes you to an ever-evolving barrage of malware and phishing, not to mention SQL injection, cross-site scripting, and man-in-the-middle attacks.

Are You CyberSmart?
Given how many free antivirus solutions are available, the number of survey participants who still don’t use any device protection was much higher than we expected. (Do keep in mind, however, that a large number of the free solutions come with potentially unwanted applications in tow. When it comes to cybersecurity, you tend to get what you pay for.)
No matter which protection you choose to use, we recommend taking a few simple steps to minimize your risk of being targeted by attackers. Enabling automatic updates for your operating system, apps, and programs, and layering your Wi-Fi security are easy but effective ways to close the gap. Also, be sure to use strong, unique passwords for your sensitive accounts. Although you’ve probably heard that one before, you’d be amazed at how many people still reuse passwords between various accounts, including their banking and other financial logins.

Nearly half of users in our survey admitted to reusing their passwords. If you’re one of them, and you find yourself thinking, “but I have so many logins and it’s too hard to remember all my different passwords,” we understand. We’ve all faced this question at one time or another during the internet age. But you can use a secure password manager to ease the burden of having to keep track of so many credentials.
My Webroot, Anywhere
Whether you’re already part of the family, want to take Webroot SecureAnywhere® for a free test drive, or purchase, we provide an online management account where you can centrally control your various connected home and mobile devices (and also manage your passwords.) If you haven’t already, take advantage of our advanced protection features today by setting up your My Webroot Anywhere account.

by Blog Staff | Mar 13, 2017 | Home + Mobile
News of yet another breach at Target or Yahoo seems pretty commonplace these days. Sometimes, the frequency of big, newsworthy hacks can make us forget about more personal threats we face: the people close to us who have easy access to our financial info, social media accounts, online identity, and even our computer password.
Exponential growth
According to Pew Research Center, the use of social media has seen tenfold growth over the last decade, with nearly 68% of U.S. adults at the end of 2016 reporting they have a Facebook account (let alone any of the other social media outlets, such as Twitter, LinkedIn, Instagram, etc.) This growth represents a turning point in the way we consume news and share information with our friends and family members. But as the world becomes increasingly connected, it’s also becoming increasingly hackable.
In a survey conducted by the University of Phoenix, it was found that 70% of social media scams in 2016 were shared manually, meaning people voluntarily and unwittingly shared posts that linked to malicious or affiliate sites. Moreover, the study found that 9 out of 10 people limit their personal information shared on social media due to fear of being hacked.
9 out of 10 people limit their personal information shared on social media due to fear of being hacked.” – Survey results, University of Phoenix, 2016
Friends don’t let friends get hacked
To increase your personal security when browsing and sharing online, we recommend you take just a few simple steps.
Enable an automatic lock on your computer.
It sounds so simple, right? But seriously, adding a lock to your computer will keep friends and foes alike from accessing your everyday accounts that you may have forgotten to close or sign out of. We recommend rotating your Windows or Apple password and making it unique and very different from others that you may use on financial or data sensitive accounts.
Use a secure password manager.
They’re easy to find and easy to use. So what’s standing in your way? Using a password manager like Google Chrome’s built-in features or the Webroot SecureAnywhere password manager enables another layer of protection that you can sign out of when you’re done browsing or paying your bills. This will also help keep you from using the same password across all of your accounts for ease of access.
Don’t enter passwords on other people’s computers.
Be wary of logging into your social media accounts on your friends’ computers. You might forget to click “no” or “never” when prompted to save your login credentials, and you wouldn’t want an embarrassing Snap or Facebook post to haunt you.
If your password gets hacked
First, don’t panic, but don’t hesitate to take action either. Change all relevant passwords immediately, including any to other accounts where you may have reused the same credentials. Inform your friends and family members immediately of the situation, and to disregard messages or posts that were sent from your account during the period of exposure. Finally, don’t forget to notify the support team for the associated social network so that they can investigate and help prevent others from becoming victims of the same types of attack.

by Connor Madsen | Mar 10, 2017 | Industry Intel
The Cyber News Rundown brings you the latest happenings in cyber news weekly. Who am I? I’m Connor Madsen, a Webroot Threat Research Analyst, and a guy with a passion for all things security. Any more questions? Just ask.
Microsoft Services Go Offline
Was I the only one who wasn’t able to access my Xbox Live account earlier this week? Once again, Microsoft services were rendered inaccessible to users due to an issue with their authentication servers. The service interruption affected Outlook, Skype, and even Xbox Live not recognizing correct credentials, as we would attempt to log into the services. Fortunately for us, most services were promptly restored to working order and we were able to game-on.
Satan Ransomware Offers New Service
We all know that ransomware isn’t a new topic (nor one that is going by the wayside), but as new variants are created, the attacks are becoming more sophisticated. With the Satan variant, malicious actors are employing new tactics. I was surprised to learn that the latest evolution introduced a service signup sheet to begin running your own ransomware campaign. Scary, right? Now we have entrepreneur malware authors refining their skills and creating ransomware. The malware authors providing this service gain revenue by taking 30% of the earnings from everyone that uses the tool to distribute ransomware.
Anonymous Decreases Dark Web Activity by 20%
Did you think Anonymous was on vacation? Well, they’re rested and back to playing Robin Hood. Anonymous took down over 11,000 Dark Web sites and the majority of sites in question were distributors of child pornography or offered access to illicit drugs. Their targets were also responsible for the leak of over 380,000 user records.
Smart Utility Readers Failing to Read Anything
Our society is becoming more connected and ‘smart’ every day but sometimes things go wrong. Over the last four months, EDF customers were paying next to nothing for their energy bills. As it turns out, the smart meters weren’t so smart and were failing to report energy usage data. Customers will receive updated bills as they’re charged for the energy usage that failed to send.
WikiLeaks Releases Immense CIA Data Vault
Don’t you love hearing about new ways our government is spying on us? If so, you’ll love what’s next. WikiLeaks has released an enormous trove of information regarding tools and methods used by the CIA to spy on us through our devices (again). By copying tactics used by large-scale malware samples, the CIA has created various tools to bypass secure messaging encryption or even turn IoT devices into spies! Creepy, right? And thanks to the selfie, we have two cameras that they can use.

by Tyler Moffitt | Mar 9, 2017 | Home + Mobile
The convenience of having some kind of internet connection on more and more of the devices we use each day is undeniable. However, without proper security vetting, this convenience may come at a hefty price. In the past year alone, we’ve seen millions of routers, DVRs, IP cameras, cars, and more get hacked and either ransomed or hijacked for illegal purposes. This is mostly because the vendors of these devices only focus on functionality and the “set it and forget it” mentality. The next big IoT device type on the high-risk radar might not be what you expect… It’s toys.
Just last month, almost a million CloudPets.com accounts were compromised which contained 2 million voice recordings of kids and their families. This data—which is currently being ransomed—was taken from an unsecured MongoDB installation. There was no password or authentication required to access the widely available MongoDB on port 2701 at 45.79.147.159. Anyone who tried to connect had access and could access as much data as they wanted. It was only a matter of time before threat actors decided to take the data and delete the original copies from the server. In fact, the MongoDB currently has over ten thousand unsecured servers from which data has been stolen and held for ransom.
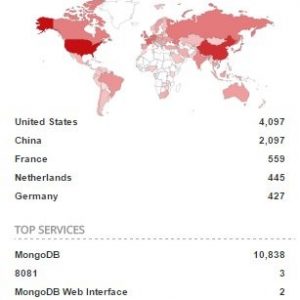
The CloudPets breach is yet another in a long list of poorly secured connected devices. Germany has already banned My Friend Cayla dolls, having classified them as espionage devices. Anyone selling the toy may be subject to a fine of up to 25,000 € for anyone who sells the toy. Barbie dolls are also on radar, since the Hello Barbie doll made headlines a couple of years ago. The doll was easily hackable and would reveal users’ system information, Wi-Fi network names, internal MAC addresses, account IDs, and even MP3 files. Aside from the sheer creepiness of hacking a children’s toy, this type of sensitive information can be used by cybercriminals to gain entry into a user’s more high-value accounts. The ease with which an attacker can access users’ details, including passwords, can give them a starting point to infiltrate other accounts, and sensitive family information can be used to guess passwords and secret questions.
Are hackers toying with your data?
We continue to witness a growing number of attacks with extortion as their goal. They begin with a simple but effective brute force assault from RDP to MongoDB and are now on to MySQL, and it won’t stop there. As long as such protocols, tools, and software are installed without adequate security measures, new breach stories will continue to make the news. Vendors of all IoT devices must ensure that they properly secure their devices and the information they collect.
Beyond the vulnerabilities the backend databases that support these IoT devices comprise, we have also been seeing remote exploitation of the actual toy device via Bluetooth Web API. Any user with a computer or a phone can connect to the CloudPets plushie without any authentication, and can then control the toy. Using the built-in microphone, an attacker can send and receive recorded messages to and from the toy, and they don’t even have to be inside the house. Experts in the field are already issuing warnings as to the privacy risks associated with allowing websites to connect to devices via Bluetooth. The CloudPets situation is a prime example of connected device manufacturers being grossly negligent towards the security of their products, and only focused on functionality (and, therefore, saleability.)
There’s a smarter way to play
To mitigate these types of risks, vendors need to conduct regular risk assessments and security vetting. They need to understand what does and does not need to be internet-facing within the organization. The items that do need to connect to the internet should be protected accordingly, starting with checking and improving on default settings. Authentication levels for each product need to be investigated and possibly enhanced to require two-factor, given that default options aren’t always the most secure. Where possible, access should be restricted based on policy, and vendors must investigate whether VPN and tunneling protocols would work for a particular use case. It’s essential to keep installations up to date. Additionally, vendors need to regularly review the setup configurations, look for unexpected or undocumented changes, and review the listed administrator accounts as a standard routine. In addition, consumers must be educated on the potential for these devices to generate and store sensitive data, as well as how to use good security practices to ensure their information stays safe. Although we can never make ourselves 100% secure, we should give ourselves a fighting chance.
Once a vendor or organization has set up what it believes to be the best defense, it cannot simply forget about it. Plans need to be in place for when a breach does occur so data can be recovered as quickly and efficiently as possible. This means creating and executing a well-divided, regularly-tested, air-gapped backup strategy. It could mean the difference between a breach being little more than a learning experience, versus resulting in devastating losses from which the business may not recover. It’s also important to make sure all employees are aware of what to do when things go wrong, as time will be of the essence. Each employee must know who needs to do what, when, where and how, from the incident responders to PR. Because the modern threat landscape continually changes, the only way to achieve remotely effective protection is not to sit back and relax, but to continue examining, refining, and improving upon security practices.

by Karina Edmondson | Mar 8, 2017 | #LifeAtWebroot
In honor of International Women’s Day, we hosted our quarterly Women of Webroot meeting this afternoon at our World Headquarters in Broomfield. Women of Webroot brings together women from all parts of our business to celebrate wins and provide support for issues women in tech may face.
Although there are more women in technology-related positions now than in previous years, the tech industry is still largely male dominated. This divide underscores the importance of a sense of workplace community and support, as well as a place where your voice will always be heard.
Empowering others to speak up.
Attendees shared different stories of inappropriate or uncomfortable situations they’ve faced in the workplace and their strategies for addressing them. The truth is that speaking up about inappropriate comments or behavior can be just as uncomfortable as experiencing them in the first place.
Here are some of the approaches we heard today.
- The straightforward approach: “It’s not okay for you to speak to me that way.”
- Taking a moment to step away from the situation before responding
- Scheduling time with someone individually to address the comment
- Giving someone perspective on what they’ve said by saying it back to them
- Focusing on the facts
- Encouraging and empowering others to speak up as well
- Asking direct questions to get to the heart of the matter, and give yourself time to collect your thoughts
Own your voice.
All in all, some great suggestions came out of our time together. Hearing how my teammates have been successful in addressing challenging situations was inspiring. The important thing is to find your voice and find the approach that is most comfortable for you. Although these can be awkward conversations to have, it is only by raising our voices, drawing attention, and being heard that we can build awareness within our teams, our networks, and ourselves. To achieve and maintain an open culture, we each have to take an active role. We are fortunate to have such a strong internal network that we can turn to for strength, and look forward to its continued growth.






















